Blockchain for the supply chain refers to the implementation of blockchain technology in the management and tracking of goods and information. It provides an immutable, shared ledger wherein companies can record their production updates.
Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency in the following ways:
- Immutable Recordkeeping
- Real-time Tracking
- Data Sharing across all stakeholders
- Smart Contracts
- Authenticity of products and documents verification
Outsourcing blockchain-based supply chain services from a specialized provider like Oodles Blockchain can offer several advantages:
- Expertise: Access to a team of experts experienced in blockchain technology and supply chain integration.
- Cost Savings: Avoid the costs associated with building and maintaining an in-house blockchain solution.
- Time Efficiency: Faster deployment and implementation of blockchain supply chain solutions.
- Scalability: The ability to scale services up or down based on your specific needs.
- Focus on Core Competencies: This allows your organization to focus on core business activities while experts handle blockchain integration.
Blockchain can prevent counterfeit products in the supply chain through its transparency and traceability features:
- Immutable Records: Every product is recorded on the blockchain at each stage of the supply chain, making it difficult for counterfeit goods to enter undetected.
- Smart Contracts: Automated verification processes can ensure that products meet quality and authenticity standards before they proceed in the supply chain.
- Authentication: Blockchain can be used to verify the authenticity of products using Quick Response (QR) codes, Radio frequency Identification (RFID) tags, or other methods.
- Real-time Tracking: Real-time tracking allows for the immediate identification of discrepancies or unauthorized changes in product information.
Blockchain can address various challenges in the supply chain, including:
- Transparency: Providing real-time visibility into the movement of goods and data.
- Counterfeiting: Preventing counterfeit products from entering the supply chain.
- Traceability: Allowing for the tracking of products from origin to destination.
- Efficiency: Streamlining processes and reducing delays and errors.
- Trust: Building trust among supply chain participants through secure and transparent transactions.
- Security: Protecting data and transactions from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
They can. First, they can get access to a specific level of transparency regarding the transactions that supply chain actors send to the network. Alternatively, the system's rules may also grant auditing bodies control of the system itself, depending on the use case. For instance, if audits fail, a certifier might stop a producer from issuing more digital assets that carry a certification.






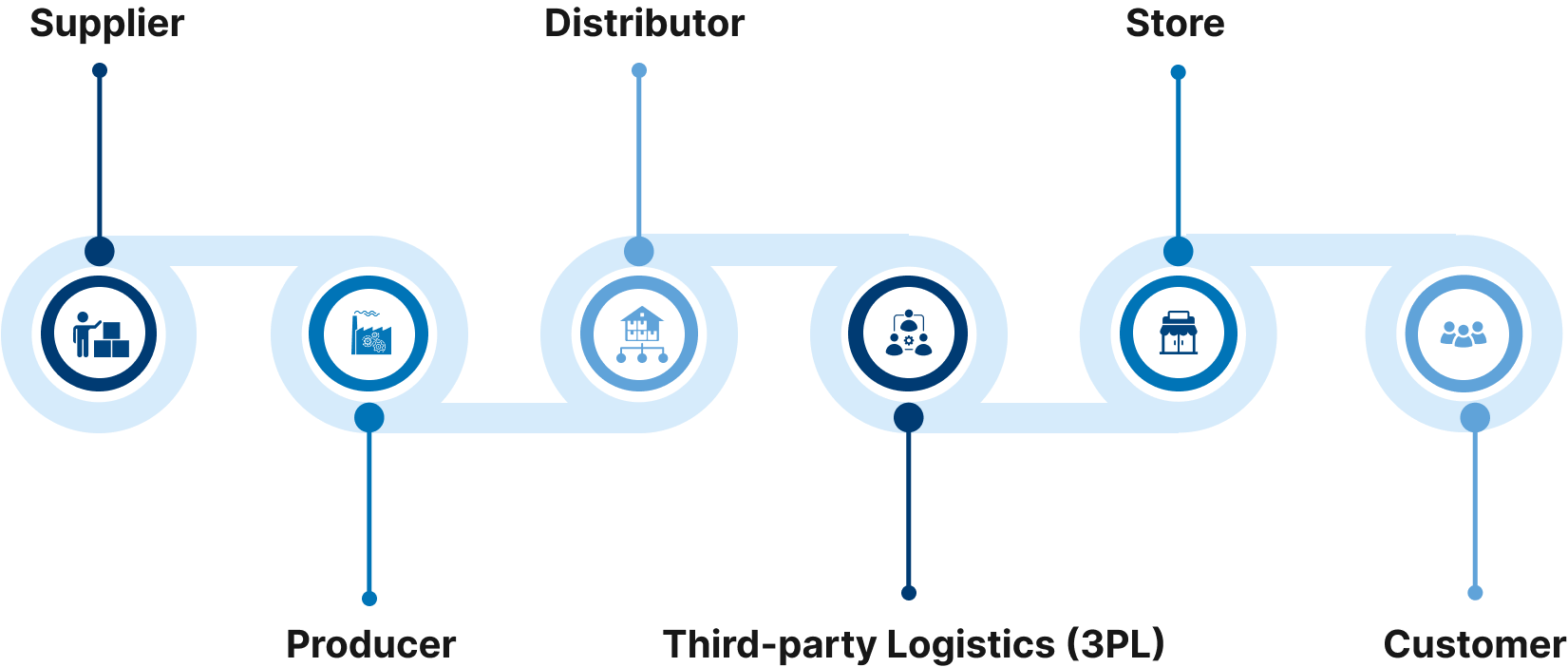
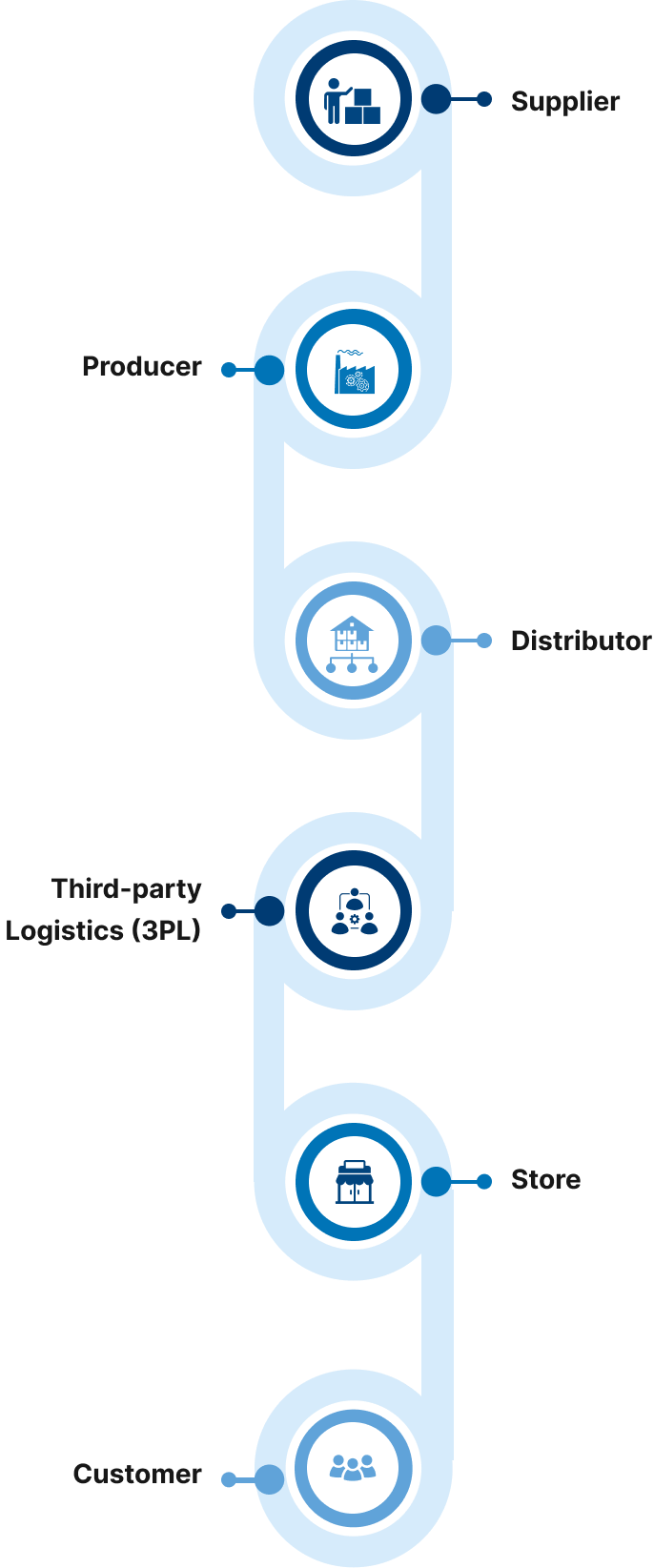




















 Blockchain Application Development
Blockchain Application Development
 Fintech Blockchain App Development
Fintech Blockchain App Development
 Hyperledger Application Development
Hyperledger Application Development
 STO Development Services Company
STO Development Services Company
 Exchange Development
Exchange Development
 Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development